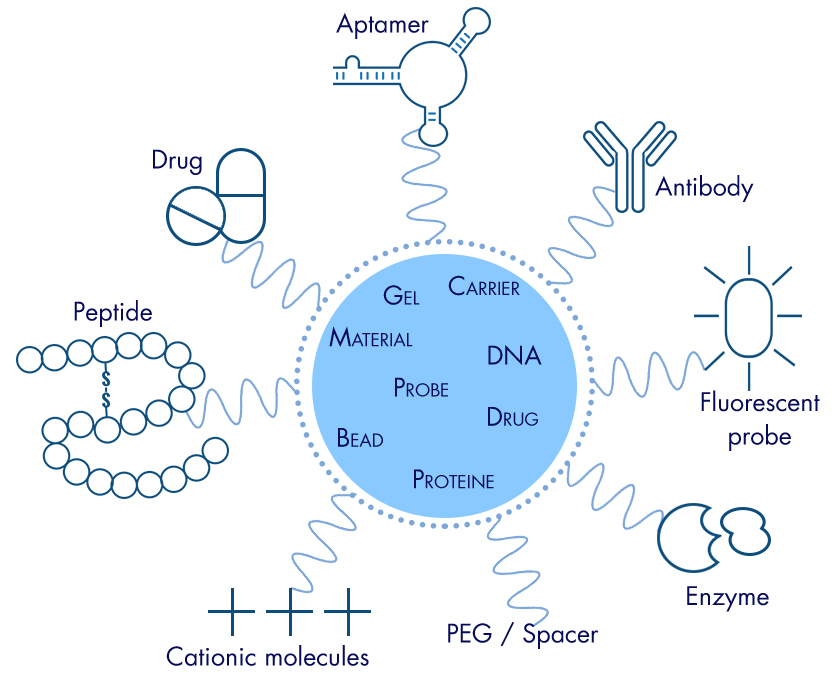
DEFINITION AND PRINCIPLES PEGylation is a chemical modification that involves conjugation of active polyethylene glycol (PEG) to a therapeutic molecule or to a delivery system (nanoparticle). Introduced in the 1970’s to improve the drug bioavailability (life time in blood, reduction of immunogenicity), these techniques diversified, encompassing various applications in organic synthesis, biochemistry, analysis, purification, functionalization of surface in material sciences (bio-, nano-), cell culture. PEGylation of a molecule can cause changes in physicochemical properties such as increase in hydrophilicity, size, and molecular weight, changes in conformation, and steric hindrance of intermolecular interaction. Studies have shown that PEGylation of targeted drug delivery may decrease clearance and enhance delivery of peptide and protein molecules. PEGylation, by increasing the molecular weight of a molecule, can impart several significant pharmacological advantages over the unmodified form, such as improved drug solubility, reduced dosage frequency, without diminished efficacy with potentially reduced toxicity, extended circulating life, increased drug stability, and enhanced protection from proteolytic degradation; peglyated forms may also be eligible for patent protection. ADVANTAGES OF PEGylation Improved the molecules properties Solubility and/or hydro solubility are increased Steric and hydrodynamic changes Compatibility with any chemistry of conjugation/labeling/functionalization Improved pharmacokinetics Increased half-time Reduced degradation Reduced clearance Reduced maximal drug concentration Lower peak-to-through in ratio plasma drug concentration Restricted volume of distribution Decreased immunogenicity Decreased adverse effects Pegylation agents are polar, hence soluble in aqueous solutions that render them suitable for biological or biochemical applications. Superior concentrations can be performed during the conjugation step, allowing higher coupling ratios. More interestingly, the hydro solubility is carried by the spacing arm, so the hydrophilicity is held by the formed conjugate. 5. Applications of PEGylation are numerous DISADVANTAGES OF PEGylation Reduced in vitro activity Steric interference of core protein to the target receptor Interference with protein binding site or conformation PEGylated PHARMACEUTICALS The attachment of an inert and hydrophilic polymer was first reported around 1970 to extend blood life and control immunogenicity of proteins. Polyethylene glycol was chosen as the polymer. In 1981 Davis and Abuchowski founded Enzon, Inc., which brought three PEGylated drugs to market. Abuchowski later founded and is CEO of Prolong Pharmaceuticals. The first pegylated drugs approved by the FDA in the early 1990s were pegaspargase for leukemia and pegademase for severe combined immunodeficiency disorder. ADAGEN (pegademase bovine) was manufactured by Enzon Pharmaceuticals, Inc., US FDA approved PEGylated pharmaceuticals on the market have included: by Babayeva N. References: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PEGylation https://www.researchgate.net/publication/262193813_Nanomedicines_in_the_treatment_of_hepatitis_C_virus_infection_in_Asian_patients_Optimizing_use_of_peginterferon_alfa https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18778113 http://www.interchim.com/blog/pegylation/ https://creativepegworks.wordpress.com/2015/04/05/fda-approved-pegylated-drug/
If this page is in your subscriptions, then it will be removed. You will not see this page. If you want to unblock a user, go to the settings, the list of blocked users and click unblock